Geog 495: GIS Database Design
9/29/05
Data vs. Information
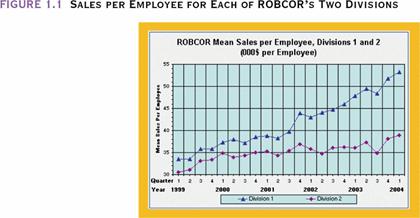
Example A
A pile of sales inventories for item a and b à you have found out they are increasing, and the gap between two items is widening by graphing trends
Example B
A collection of satellite images à you compare the urban land use from year 1973 to year 2000, and found out that it has expanded (i.e., urban sprawl?)
http://www.grid.unep.ch/activities/global_change/atlas/images/LasVegas.jpg
Processing data helps you to reveal the meaning, or even help you identify phenomenon you couldn’t see otherwise. What’s the role of database design on this transformation from data into information?
Data vs. database
The difference
can be viewed from set theory: which is bigger? Actually more than that
can be viewed from end user’s view: does it serve a specific purpose of end users?
Both requirements should be met to determine which is database
Database vs. database
management system (DBMS)

DBMS is a collection of programs that manages the database structure and controls access to the data stored in the database; allows for sharing data among multiple applications or users (e.g., Oracle, Informix, SQL Server)
Spatial DBMS: specialized DBMS to meet the requirements of spatial data (SC1:10)
e.g., ArcSDE, Spatial Data Blade, Spatial Data Cartridge
DBMS vs. database
system
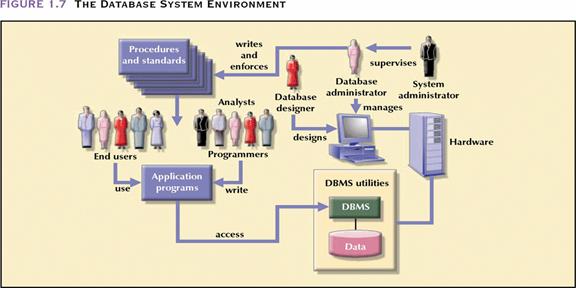
Database system is composed of five main components
(1) hardware (2) software (3) people (4) procedures (5) data
Need for database
system
Limitations of file systems: data redundancy, data dependency
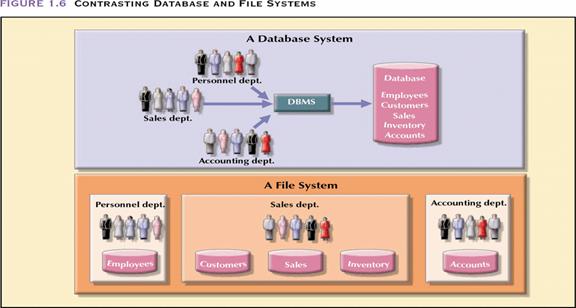
Data redundancy: different and conflicting versions of the same data appear in different places; lead to data inconsistency
Data independency: separation of data from programs that use the data
Different types of
database
· Number of users
Ø Single-user
Ø Multiuser
Ø Workgroup
Ø
· Database site location
Ø Centralized
Ø Distributed
· Database use
Ø Transactional (production) database
Ø Data warehouse database
Why database design
is important
DB design is like blue print for building house
Good applications can't overcome bad database designs
Lab
Open files P:\geog495aut05\Ch01_Problems.mdb
Open PROB_1_01 in the table
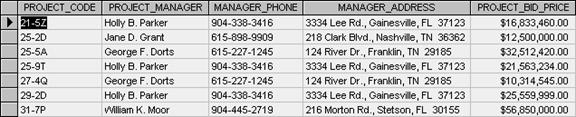
1. How many records does the file contain, and how many fields are there per record?
2. What problem would you encounter if you wanted to produce a listing by city? How would you solve this problem by altering the file structure?
Open PROB_1_05 in the table
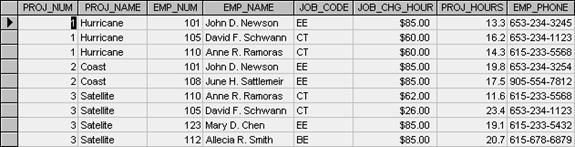
3. Identify and discuss the serious data
redundancy problems exhibited by the file structure.
4. Identify the different data sources in the file you examined.