ODBC (Open Database
Connectivity)
Short for Open DataBase Connectivity, a standard database access method developed by the SQL Access group in 1992. The goal of ODBC is to make it possible to access any data from any application, regardless of which database management system (DBMS) is handling the data. ODBC manages this by inserting a middle layer, called a database driver , between an application and the DBMS. The purpose of this layer is to translate the application's data queries into commands that the DBMS understands. For this to work, both the application and the DBMS must be ODBC-compliant -- that is, the application must be capable of issuing ODBC commands and the DBMS must be capable of responding to them.
From webopedia.com
In ArcGIS
This tutorial shows (1) how to access your mdb file from ArcGIS, and (2) how to geocode your table using x, y coordinates (assuming that your table contains x, y coordinates).
Usually accessing mdb file from other applications (let’s say Arc/Info or Arcview) requires you to create data source using ODBC tools (which can be found at Control Panel – Administrative Tools – Data Sources (ODBC), but ArcGIS support the direct connection through arccatalog. So you don’t need to create data source.
Copy Ch06_Review_XY.mdb from P:\geog495aut05 and past into your working folder, say C:\Temp\shwang5
Open ArcCatalog (Start – ArcGIS – ArcCatalog)
Connect to your working folder using “Connect To Folder” button ![]() (it’s
located below the menu Edit)
(it’s
located below the menu Edit)
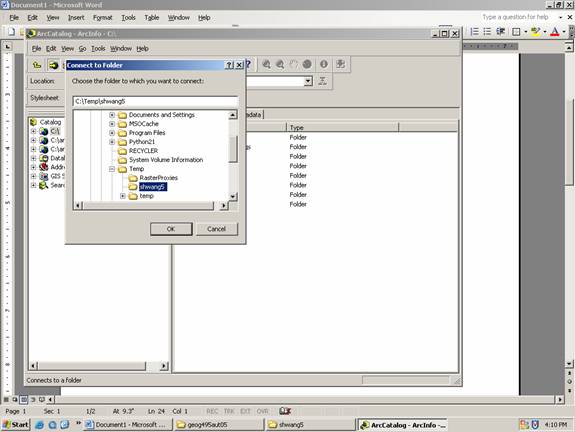
Click OK
Launch ArcMap by clicking ![]()
Click OK when ArcMap is open
Click “Add Data” tool ![]() to add tables in your mdb
file
to add tables in your mdb
file
Browse through the folder you connected, double-click the mdb file, and then double-click EMPLOYEE table.
Now EMPLOYEE table is added to ArcMap
Browse through the table by clicking Open in your right-mouse-click. The table actually contains two more fields that stores x, y coordinates of the address of each employee (it’s fictitious).
Now you’re going to geocode EMPLOYEE table using x, y coordinates
Right-mouse click on EMPLOYEE, then choose Display X, Y data
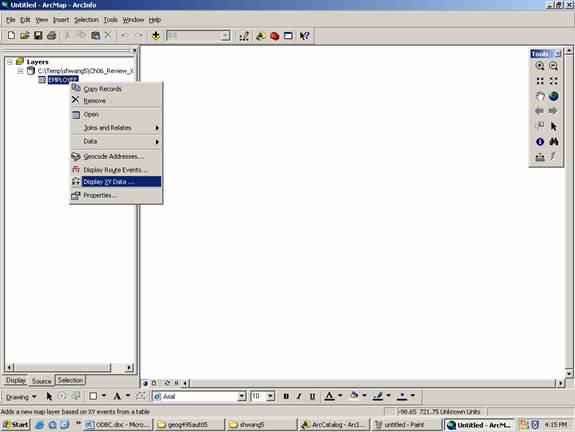
Choose X_COORD for X Field: and Y_COORD for Y Field.
In your Display XY data dialog box, choose Edit button under Spatial Reference of Input Coordinates. (This is how you choose coordinate system).
Click Select button in Spatial Reference Properties dialog
box. Choose Geographic Coordinate System – North America – North American Datum
1983.prj ( I assume this data is collected in the
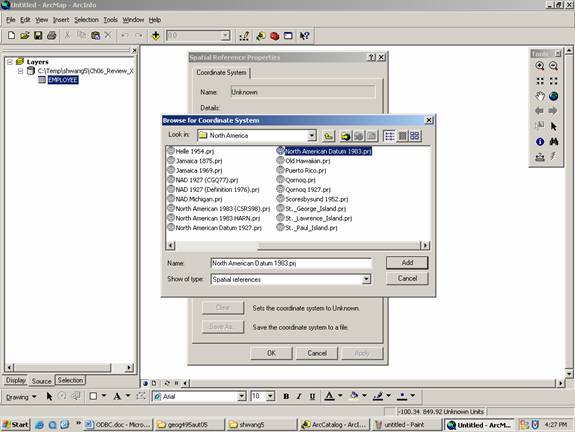
Click ADD and then OK.
Now you will see that EMPLOYEE is geocoded (geocoding means the transformation from non-spatial data to spatial data).
Export EMPLOYEE Events into shapefiles
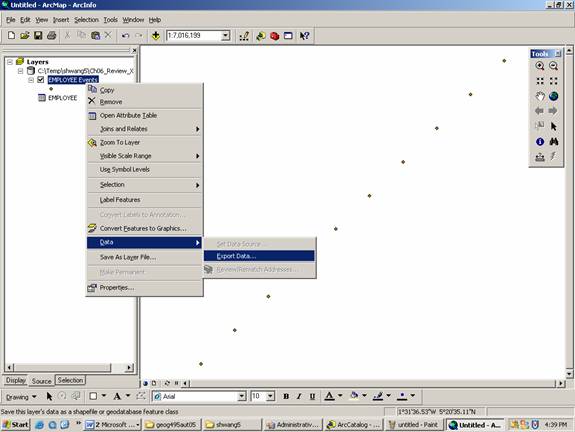
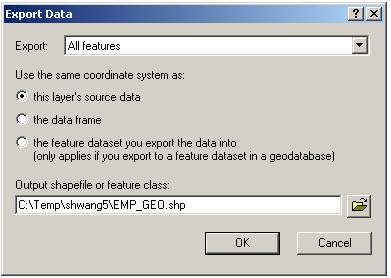
Now you create spatial data in shapefile format.
This tutorial assumes that you already collected spatial information which can be stored simply in two fields (X_COORD and Y_COORD) as it is represented as a point. But if you work on polygon data (such as COUNTRY), then you have to join non-spatial table in your mdb file to COUNTY data (which is spatial data).
In Arc/Info workstation
This tutorial shows how to access your database file (mdb) from arc/info workstation using SQL statement
1. Create data source
Before you do this, let’s assume that your mdb file is located in c:\temp\shwang5\ODBC
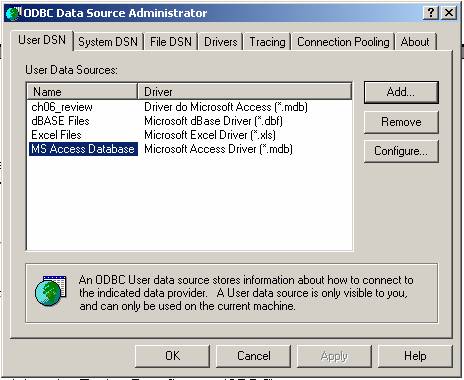
Open Control Panel – Administrative Tools – Data Sources (ODBC)
Click MS Access Database
Click Add button
Choose Microsoft mdb driver (in the middle)
Click Finish
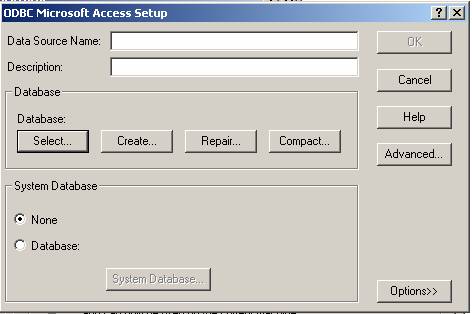
When ODBC Microsoft Access Setup, choose Select button
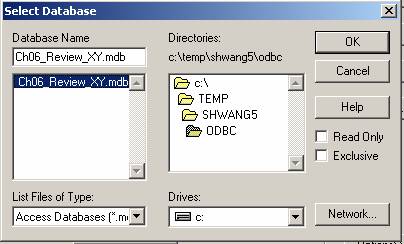
Select your mdb file, then click OK
Give data source name, say review1 at the top (you just type in)
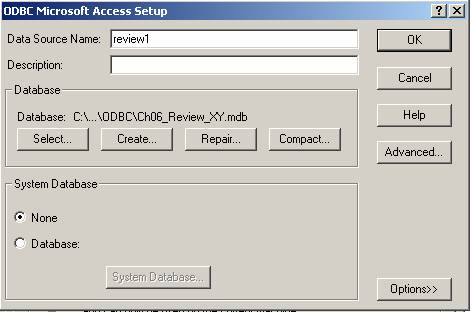
Click OK, and OK
Now you create data source named review1 which is access mdb driver.
2. Access mdb file from arc/info
Open Arc/Info workstation
Type in the following in the command line.
Connect access review1
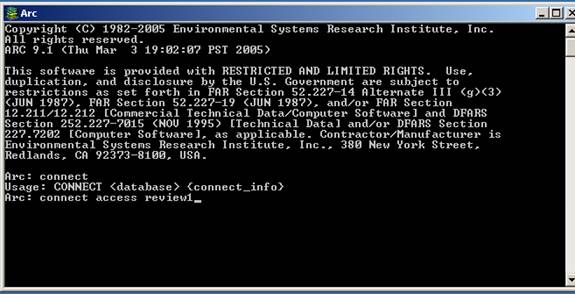
You just connect access database named review1
Arc/info command DBMSEXECUTE allows you to access your database with SQL statement
DBMSEXECUTE <database> <SQL_statement>
You put access for <database>
You put any SQL statements for <SQL_statement>
For example,
Dbmsexecute access select * from EMPLOYEE
Will list all field values from EMPLOYEE
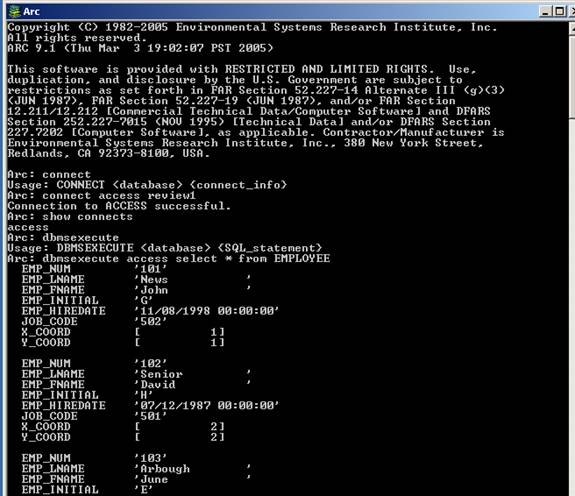
Try something else, such as
dbmsexecute
access select count(emp_num) from employee
dbmsexecute
access select emp_lname from employee where job_code = '501'
and see what happen
If you’re done, you disconnect database
Disconnect access
If you are not sure about the syntax of the command, type in help in arc/info workstation, and then type in command in index.
-- END --